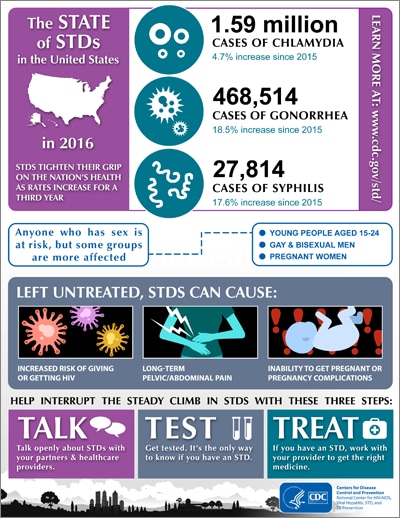
Nearly 2.3 million cases of chlamydia, gonorrhea and syphilis were reported in the United States in 2017 — more evidence of a steep and sustained increase in these reportable infections and marking another record-breaking year for STDs in the U.S., federal officials announced.
According to preliminary data released by the CDC at the STD Prevention Conference in Washington, D.C., between 2014 and 2017, diagnosed cases of gonorrhea increased 67% from 333,004 to 555,608. Cases nearly doubled among men, and increased in women for the third year in a row.
The CDC noted concerns beyond the rise in cases, noting that the threat of untreatable gonorrhea persists in the U.S. and is reinforced by reports of antibiotic resistant gonorrhea abroad.
According to the CDC, gonorrhea is resistant to nearly every class of antibiotic used to treat it, except ceftriaxone, the only effective antibiotic used to treat gonorrhea in the U.S. In 2015, the CDC began recommending a dual therapy of IV ceftriaxone with oral azithromycin to treat gonorrhea with the intent of delaying the development of resistance.
But preliminary data for 2017 shows that 4% of gonorrhea isolates in 2017 showed emerging resistance to azithromycin, the CDC said. The concern is that azithromycin-resistant genes in gonorrhea could cross over into strains of gonorrhea with reduced susceptibility to ceftriaxone, leading to a strain that no longer responds to ceftriaxone, according to the agency.
Primary and secondary syphilis — the most infectious stages of the disease — increased 76% from 17,375 to 30,644 cases since 2013. Nearly 70% of those cases where the gender of the sexual partner is known were made up of men who have sex with men.
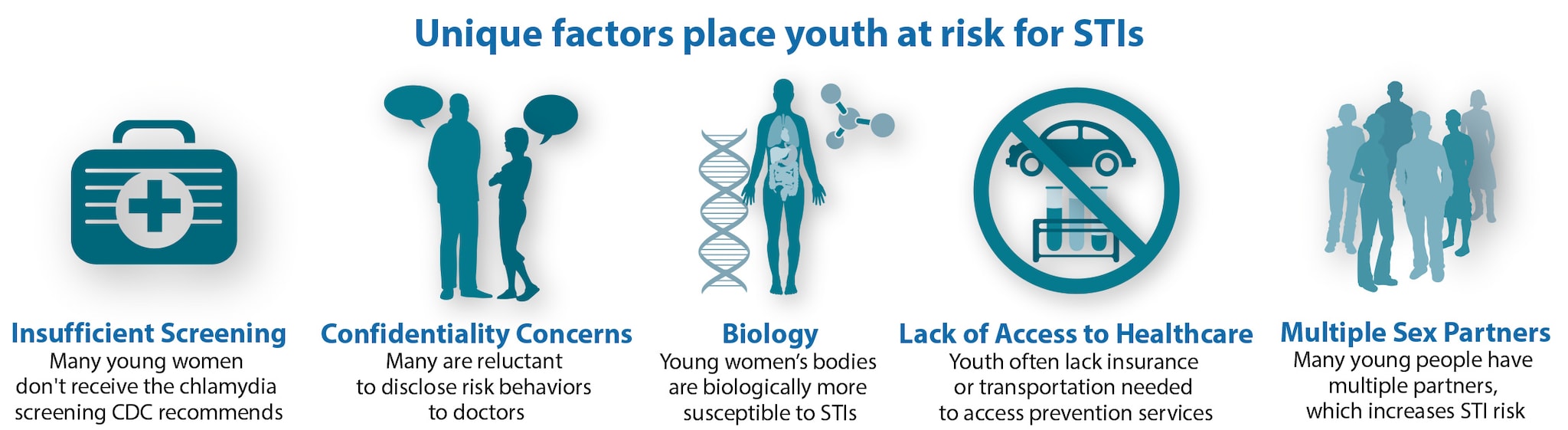
Chlamydia was the most common condition reported to the CDC, with more than 1.7 million cases diagnosed in 2017. Almost half of those cases were among females aged 15 to 24 years.
According to the CDC, most cases of STDs go undiagnosed and untreated, which can lead to severe adverse health effects including infertility, ectopic pregnancy, stillbirth and increased risk for HIV.
It’s a critical time for STD prevention.
fonte: CDC

Nenhum comentário:
Postar um comentário